Webhooks
Webhooks allow you to send data to Make over HTTPS. Webhooks create a URL that you can call from an external app or service, or from another Make scenario. Use webhooks to trigger the execution of scenarios.
Webhooks usually act as instant triggers. Contrary to scheduled triggers, which periodically ask a given service for new data to be processed, webhooks execute the scenario immediately after the webhook URL receives a request.
Make supports the following types of webhooks:
App-specific webhooks listen for data coming out of a specific app, also called instant triggers.
Custom webhooks allow you to create a URL to which you can send any data.
Creating app-specific webhooks
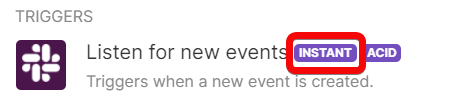
Many apps provide webhooks to execute scenarios whenever a certain change occurs in the app. These are called instant triggers. Instant triggers are marked with the label "INSTANT" in the list of an app's modules:
If an app does not provide webhooks, use polling triggers to periodically poll the service for new data.
Creating custom webhooks
To create a webhook, you must insert the Custom webhook module to a scenario.
Note
Each scenario must use its own webhook. You can not use one webhook in multiple scenarios.
Inserting webhooks to scenarios
Insert the Custom Webhook module from the Webhooks app.
In the module's settings, click Add.
Set the webhook's name and other settings, then click Save.
Make generates a URL and starts listening for requests to this URL. Send a request to this URL to have Make automatically determine the data structure for this webhook. See setting up webhook data structure below for more details.
Note
You can access the webhook's details and change the webhook's settings in the Webhooks section in the left menu.
Setting up webhook data structure
Optionally, you can let Make know what data structure to expect in the webhook request payload. Make can use data structures to validate the incoming data. If you do not set up a data structure, Make will pass the incoming data to subsequent modules in your scenario without any validation.
To enable validating incoming data, set up the webhook's data structure in one of the following ways:
Create a new data structure manually in the Data structures section.
Use an existing data structure.
You can also use the following methods to let Make know what data structure to expect.
Notice
Note that these methods do not enable data validation. The data structure set up in this way only helps with mapping the webhook data to subsequent modules in your scenario.
Create a data structure immediately after creating the webhook by calling the webhook URL with sample data in the request body.
Re-determine the data structure of an existing webhook going to the Webhook module settings, clicking Re-determine data structure, and calling the webhook URL with sample data in the request body.
If you call the webhook URL to automatically determine or re-determine the data structure, Make does not create a reusable data structure in the Data structures section. The data structure determined in this way is stored internally with the particular webhook. In this case, Make does not validate incoming data.
Scheduling webhooks processing
By default, when Make receives data on a webhook, your scenario executes immediately. If you don't want to run your scenario immediately after a webhook receives data, you can schedule your scenario to process all webhook requests periodically.
Edit the scenario which is triggered by your webhook.
Edit the scenario schedule settings.
OR
Edit the schedule settings of the webhook module.
Set up your desired schedule.
When a scheduled webhook receives data, Make stores the data in the webhook's queue. The whole queue is then processed every time your schedule criteria are met.
How Make processes webhooks
When a webhook receives a request, the system stores the request in the webhook's queue. Each webhook has its own queue. Go to the Webhooks section in the left menu to view all webhooks and their queues.
Parallel vs. sequential processing
If you are using instant webhooks, Make starts processing each request immediately as the request is received. By default, scenarios with instant webhooks are processed in parallel. Even if a previous scenario execution is still being processed, Make does not wait for its processing to complete.
You can inspect all running executions in the scenario detail. Click an item in the list of running executions to view the graphical representation of that particular execution. The execution that is currently displayed is marked with an eye icon.
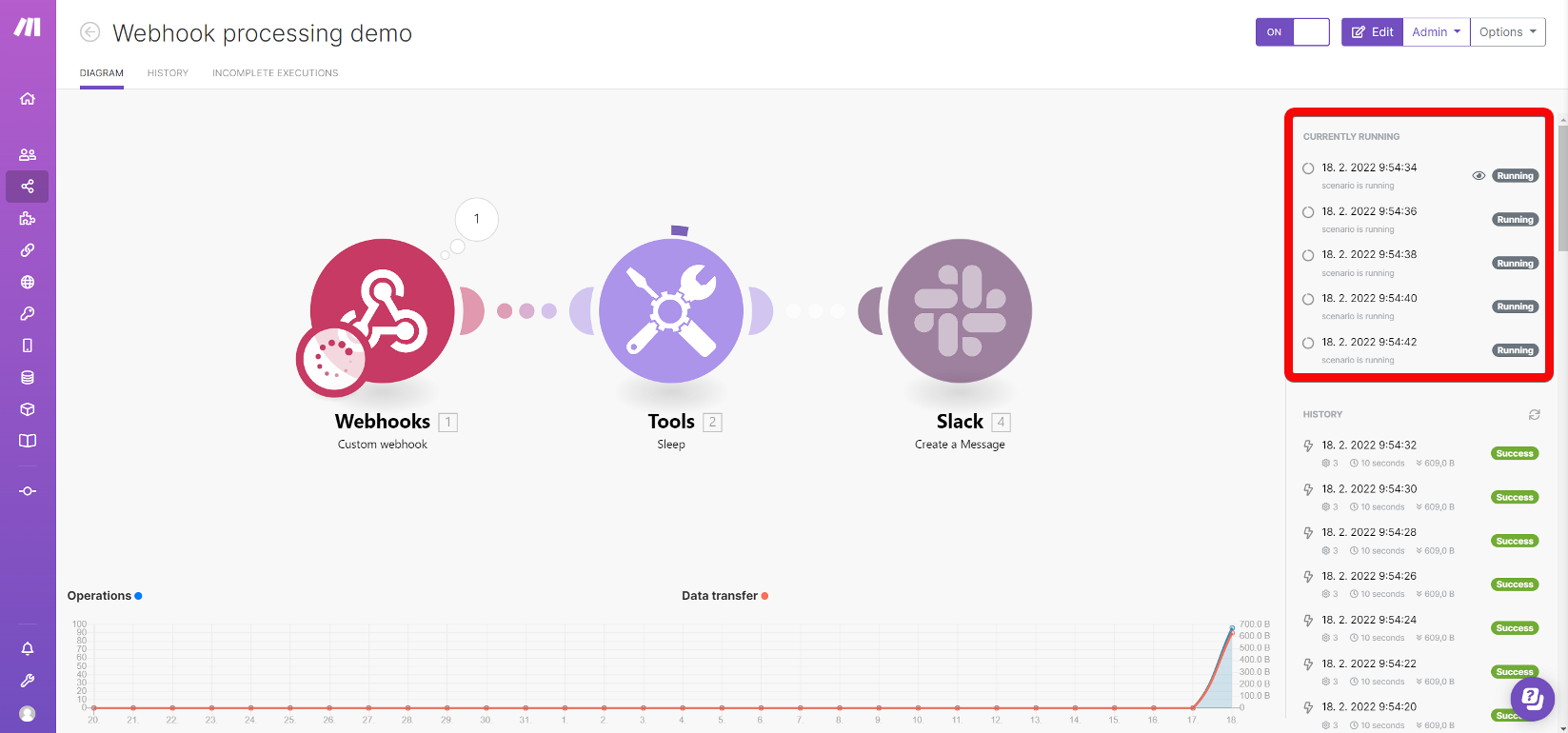
To turn off parallel processing, open the settings of your scenario and select Sequential processing. With sequential processing enabled, Make waits until the previous execution is complete before starting the next one. Also, use sequential processing when you need to process your webhook requests in the order that they came in.
Processing scheduled webhooks
If you are using scheduled webhooks, requests accumulate in the queue until the schedule criteria are met. When schedule criteria are met, Make processes the queued requests based on the Maximum number of results that you set for the webhook.
For example, if your scenario is scheduled to run every hour and your Maximum number of results is set to the default value of 2, Make processes two items from the queue every hour. If your webhook queue is filling up with requests, increase the Maximum number of results or adjust the schedule to execute the scenario more often.
Note
Instant trigger modules have the Maximum number of cycles parameter instead of the Maximum number of results.
Set the Maximum number of cycles in the instant trigger modules to get the same data processing behavior as is with webhooks and the Maximum number of results parameter.
Webhook queue details
When data arrives to a webhook and the call is not processed instantly, Make stores it in the webhook processing queue.
The limit for the number of webhook queue items depends on your usage allowance, which is a part of your subscription. For every 10,000 operations licensed per month, you can have up to 667 items in each webhook's queue. The maximum number is 10,000 items in the webhook's queue.
When the webhook queue is full, Make rejects all incoming webhook data which is over the limit.
Incoming webhook data is always stored in the queue regardless of the data is confidential option settings. As soon as the data is processed in a scenario, it is permanently deleted.
View webhook queue
To view the content of the queue, follow the steps below.
Go to the Webhooks section in the left menu.
Find the webhook whose queue you want to view.
Click the specific webhook on the list to inspect its details.
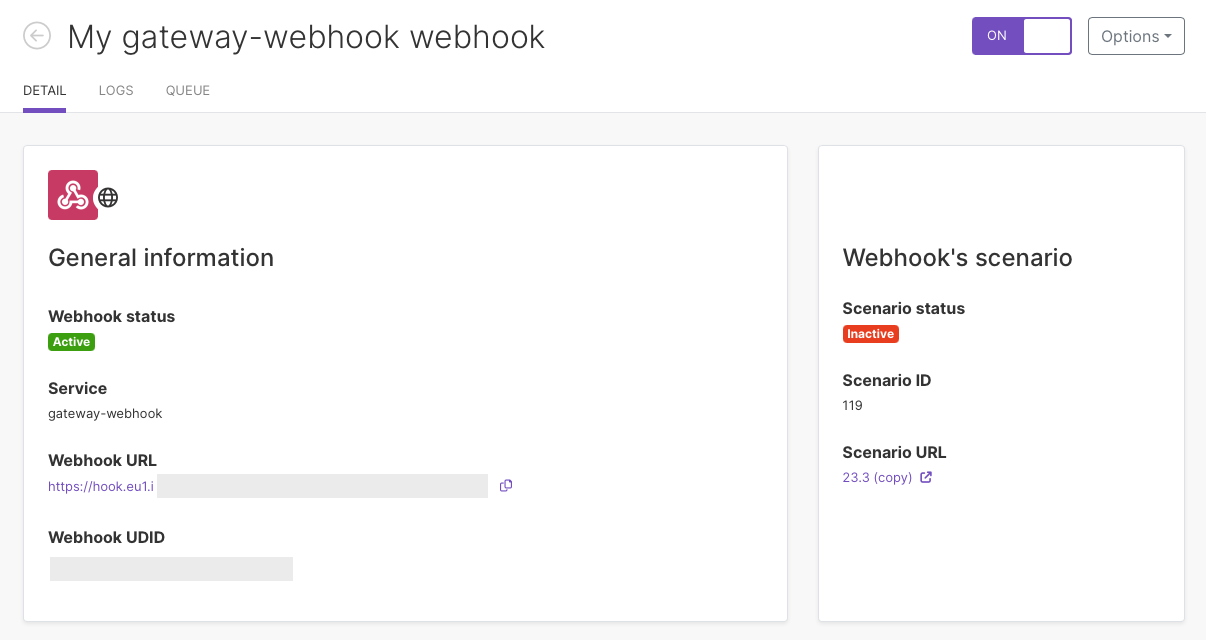
You can see:
Webhook status
Webhook URL and webhook UDID (unique webhook identifier)
Status of your scenario
Scenario ID and scenario URL
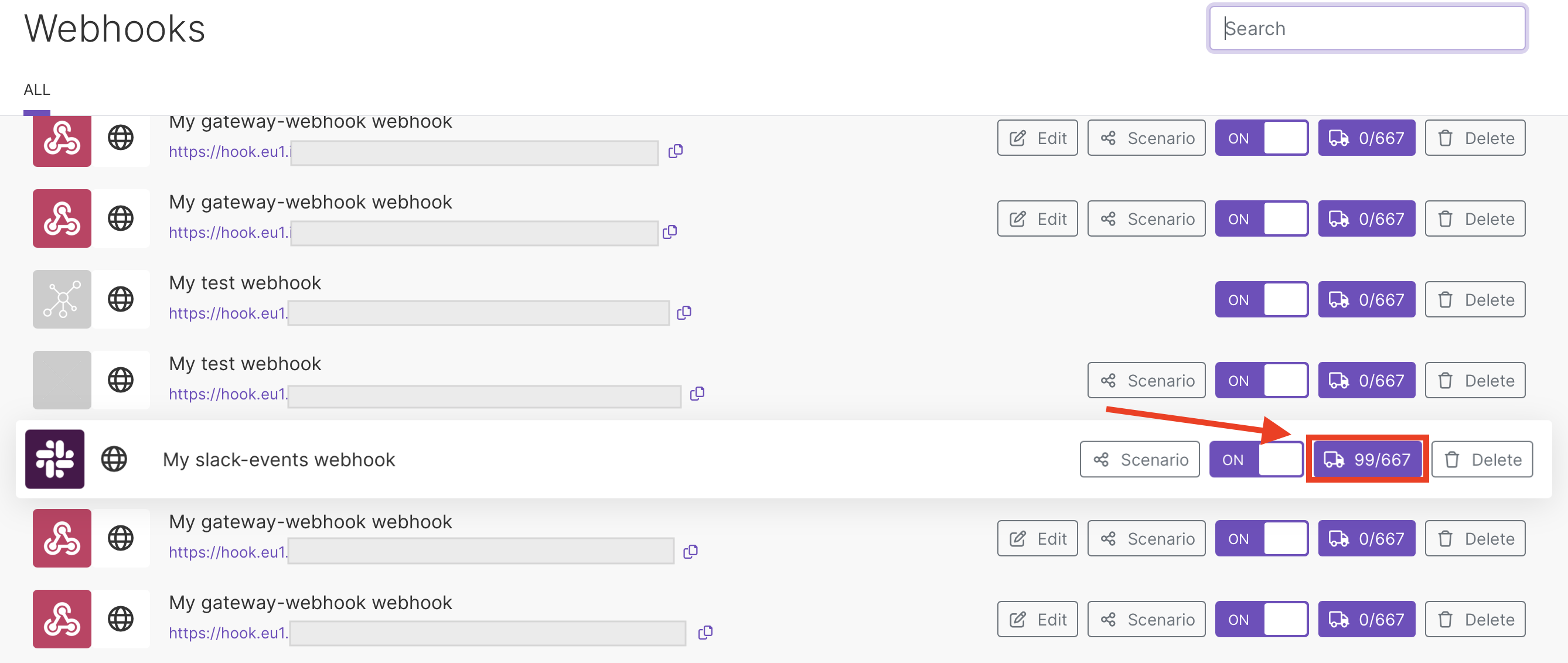
To see the webhook's queue, click Queue.
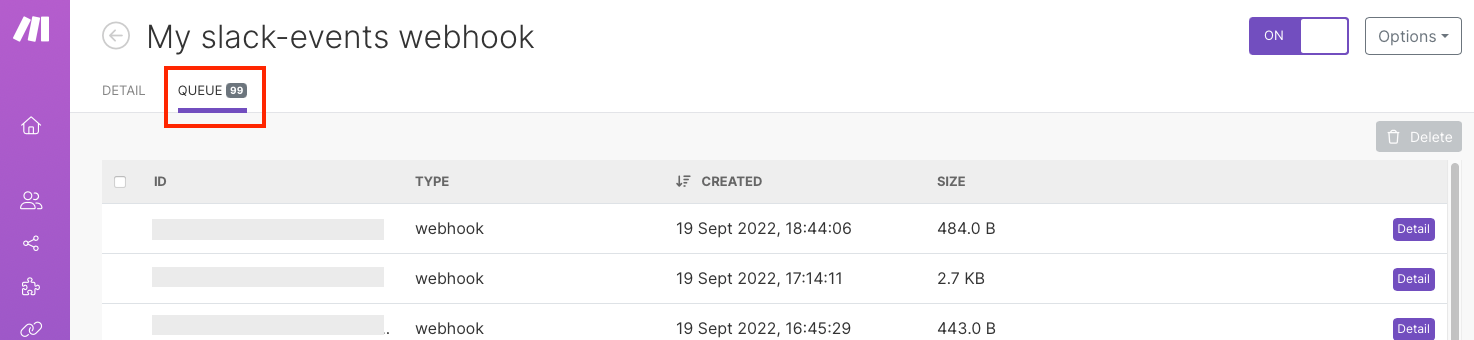
You can also click the button with the truck icon on the Webhooks page.
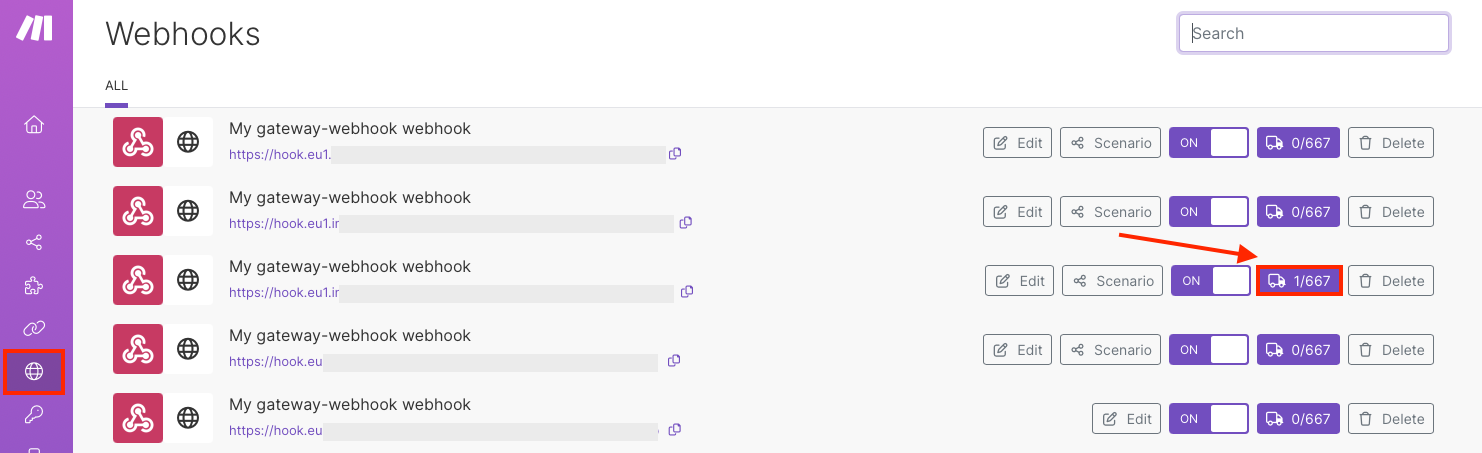
The webhook's queue displays.
Click Detail by the webhook you want to inspect.
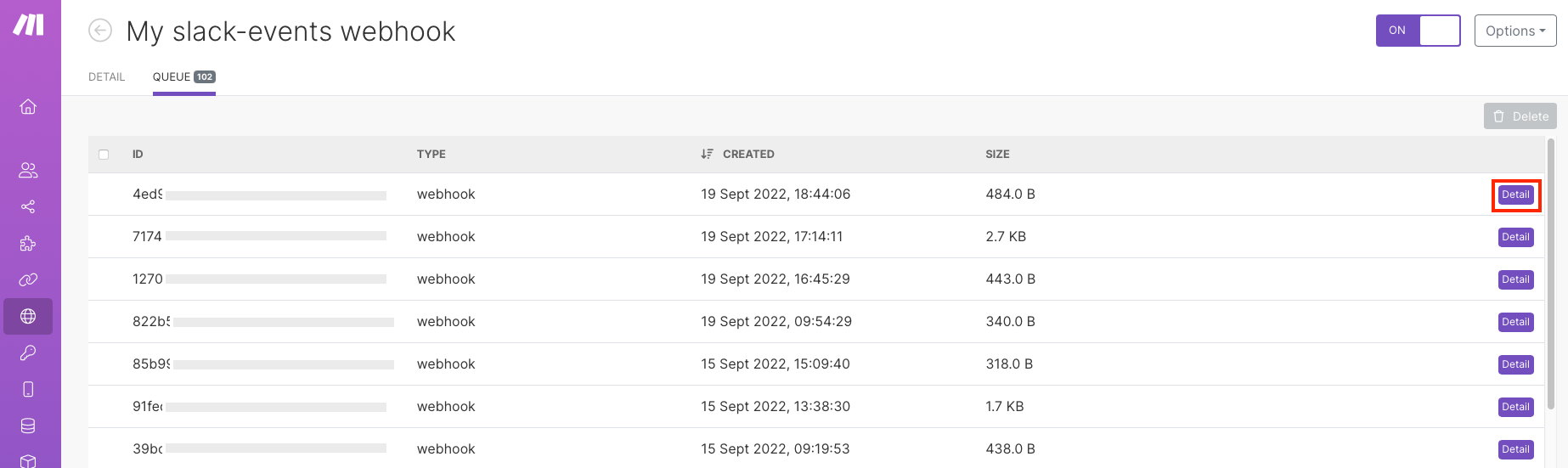
You can see the parsed items.
Expiration of inactive webhooks
Make automatically deactivates webhooks that are not connected to any scenario for more than 5 days (120 hours). The hook return 410 Gone status code.
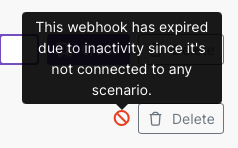 |
Delete webhook item from a queue
Go to the Webhooks section in the menu on the left.

Click the button with the truck icon to see the webhook's queue.
The webhook's queue displays.
Tick the box on the left in front of the entries you want to delete.
Click Delete selected to delete the chosen webhook(s).
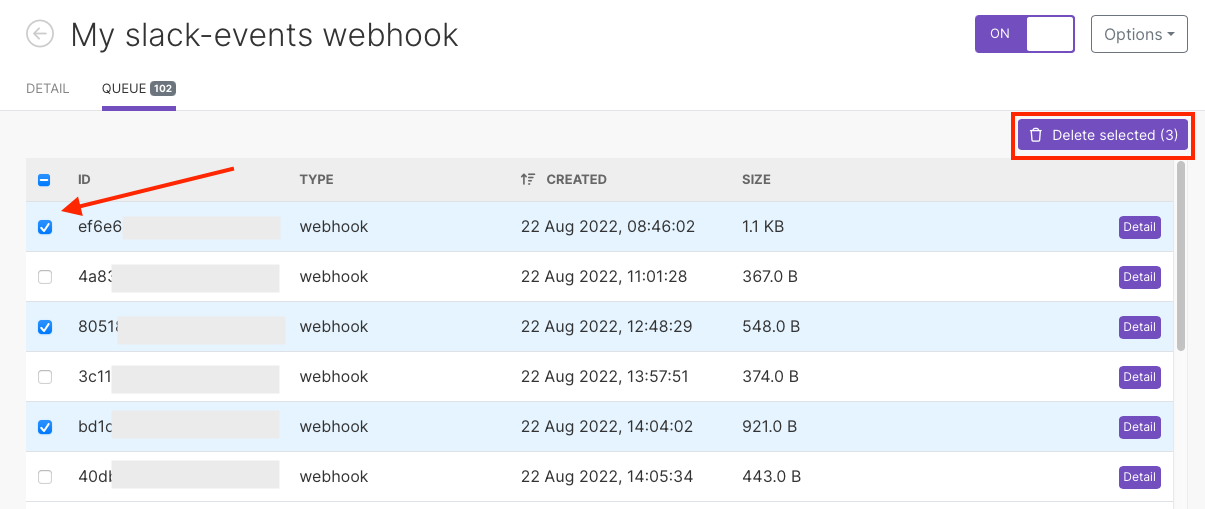
To delete all, tick the first box on the left and then Delete all.
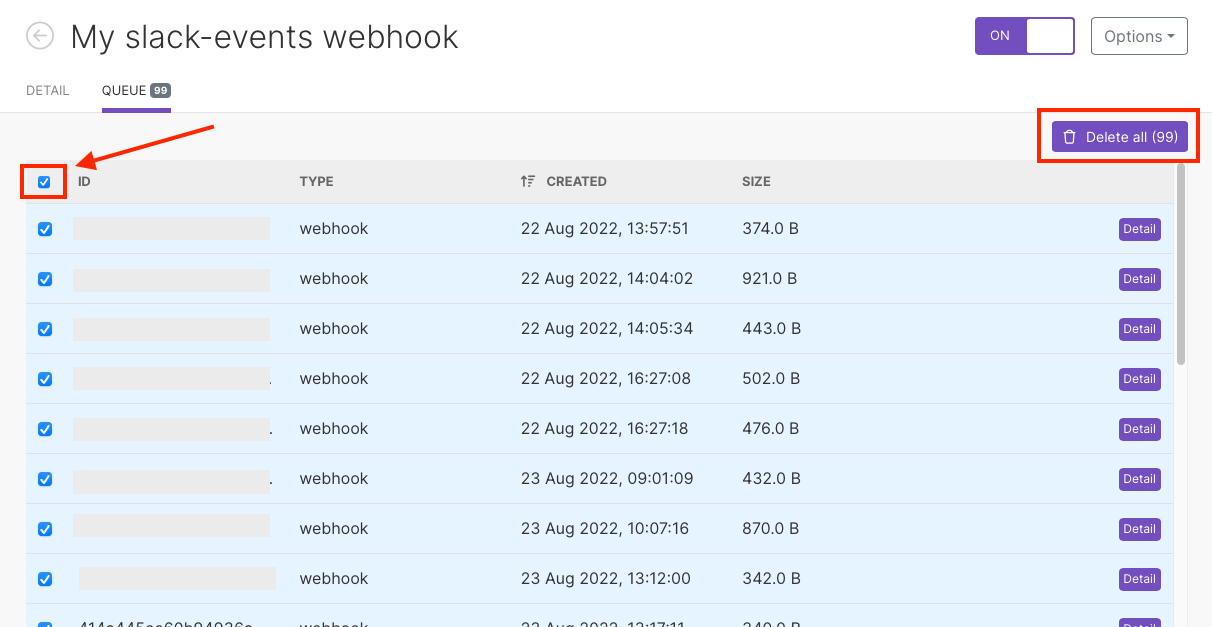
Click OK to confirm.
You have deleted the incoming webhook item(s) from the queue.
Webhook logs
Make stores webhook logs for 3 days. For the organizations on the Enterprise plan,Make keeps the webhook logs for 30 days. Make deletes logs older than other retention limit.
To view webhook logs, follow the steps below.
Go to the Webhooks section in the menu on the left.

Click the specific webhook on the list to inspect its details.
Click Logs.
You can see:
Status of the webhook call (success, warning, error, or all)
To filter the webhook logs by status, click the filter icon.
Date and time of the incoming webhook
To sort the webhook log by date and time, click the arrow.
Webhook execution log size
To see the detail of the specific webhook log, click Detail.
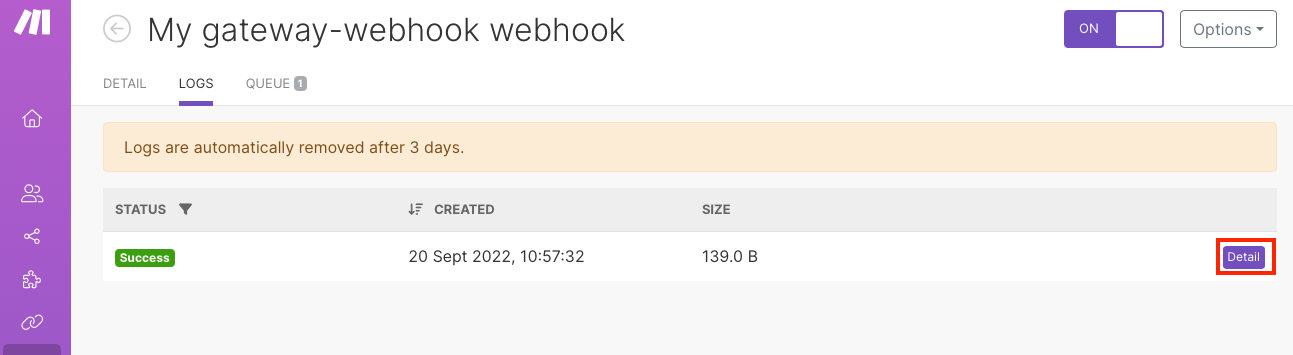
You can see:
Webhook request (timestamp, URL, method, headers, query, body)
Webhook response (status, headers, body)
Parsed items
Parsed items combine the query parameters and body of the webhook request in one bundle.
Webhook settings
To adjust a webhook's settings, click Webhooks in the left menu and Edit a webhook.
Setting | Description |
IP restrictions | A allow list of IP addresses delimited by comma. Only webhook requests that come from the specified IPs will be processed. Use CIDR notation to allow list a subnet. Leave empty if you want to allow requests from all IPs. |
Data structure | Select an existing data structure or create a new data structure for the webhook. Make will use the data structure to validate the incoming data. Requests that don't pass validation will be rejected with HTTP status code 400. |
Get request headers | Extracts headers data from the webhook request and makes the data available for mapping in the scenario. |
Get request HTTP method | Extracts the HTTP method from the request and makes the method available for mapping in the scenario. |
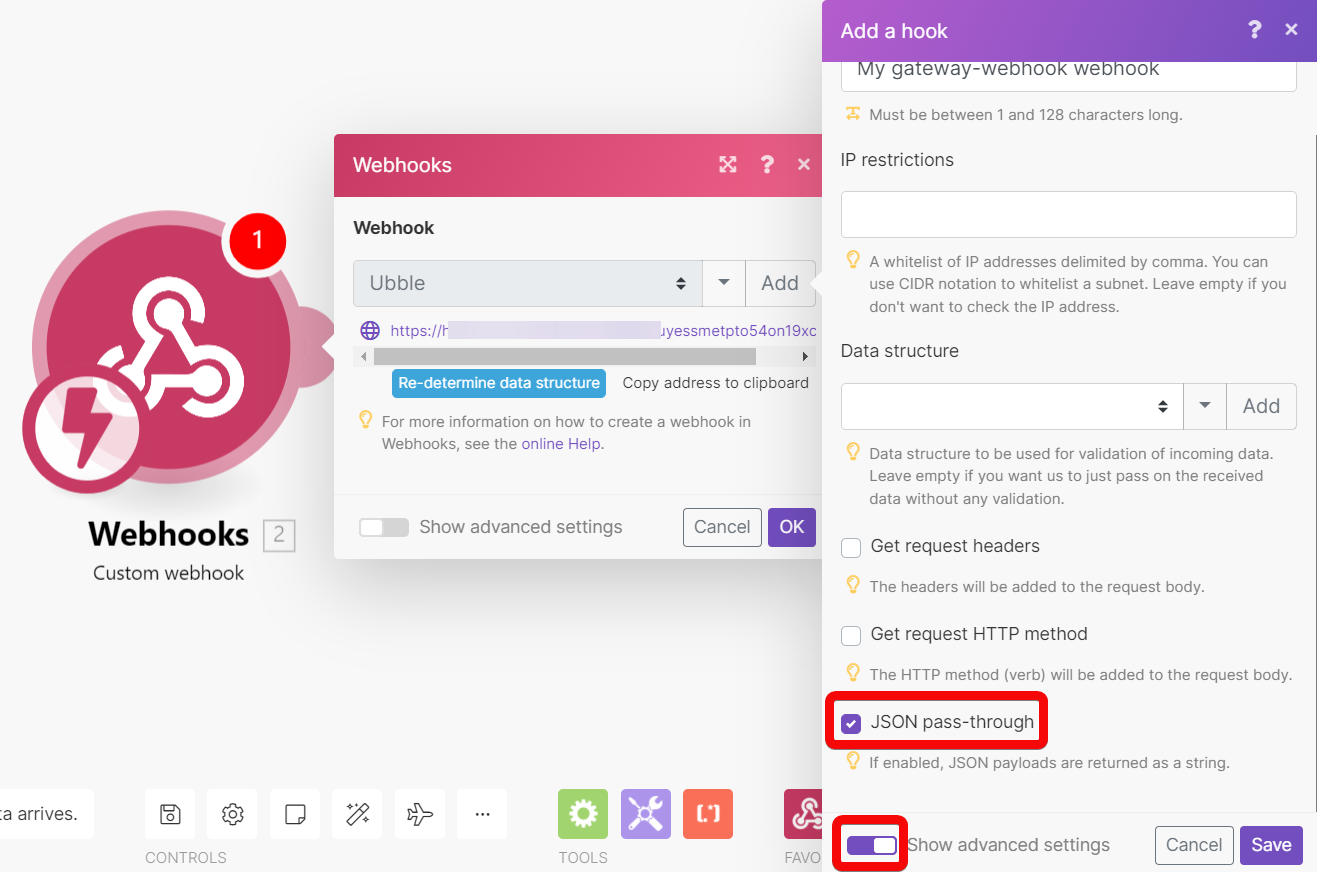
JSON pass-through | Passes JSON payloads to subsequent modules in the scenario as a text string, as opposed to breaking the payload down into mappable fields. |
Error Handling
When there is an error in your scenario with a webhook, the scenario:
stops immediately - when the scenario is set to run Immediately.
stops after 3 unsuccessful attempts (3 errors) - when the scenario is set to run as scheduled.
Supported incoming data formats
Make supports the following formats of incoming data:
Query string
Form data
JSON
If a webhook receives data in both the query string and either form data or JSON data at the same time, the system combines the data into a single bundle. If the request contains duplicate data in different formats, the query string takes precedence and overwrites the data that was received in the other formats. We recommend you do not duplicate data in query strings, form data, and JSON.
Query String
GET
https://hook.make.com/yourunique32characterslongstring?name=Make&job=automateForm Data
POST https://hook.make.com/yourunique32characterslongstring Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded name=Integrobot&job=automate
Multipart
POST
https://hook.make.com/yourunique32characterslongstring
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---generatedboundary
---generatedboundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="file.txt"
Content-Type: text/plain
Content of file.txt
---generatedboundary
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name"
Make
---generatedboundaryIn order to receive files encoded with multipart/form-data, it is necessary to configure a data structure with a collection type field that contains the nested fields name, mime and data. The field name is a text type and contains the name of the uploaded file. The mime is a text type and contains a file in the [MIME] format. The field data is a buffer type and contains binary data for the file being transferred.
JSON
POST
https://hook.make.com/yourunique32characterslongstring
Content-Type: application/json
{"name": "Integrobot", "job": "automate"}To access the original JSON, open the webhook's settings and enable the JSON pass-through option:
The maximum allowed webhook's payload size (Content-Length) is 5 MB (5.242.880 bytes) regardless of the subscription tier.
Webhook headers
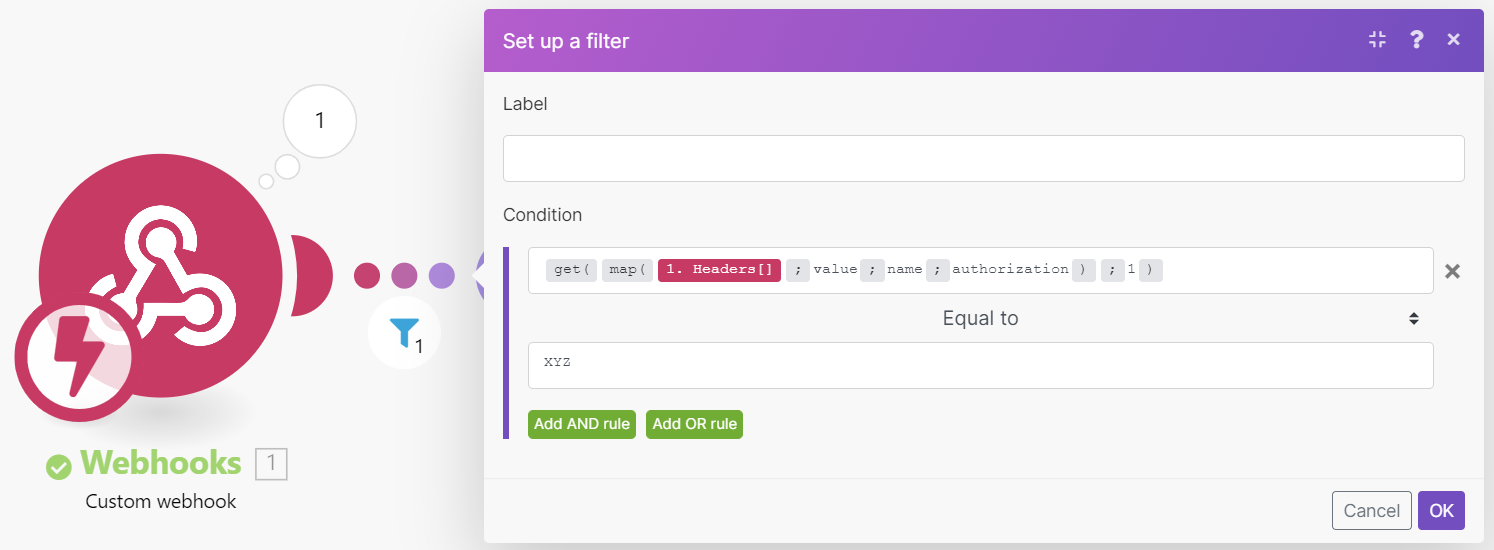
To access the webhook's headers, enable the Get request headers option in the webhook's setup:
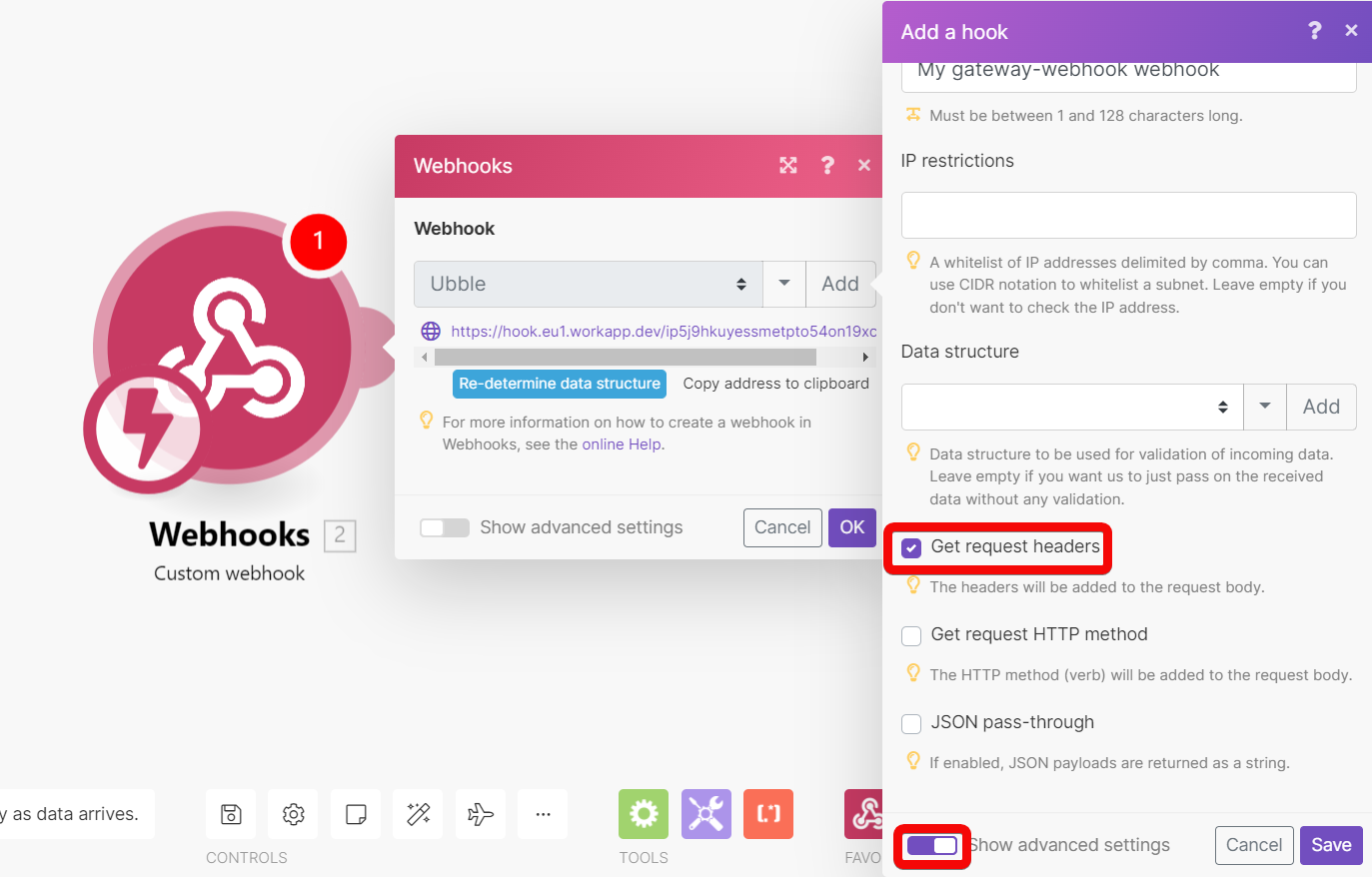
You can then extract a particular header value with the combination of map() & get() functions. The example below shows a formula that extracts the value of the authorization header from the Headers[] array. The formula is used in a filter that compares the extracted value with the given text to pass only webhooks if there is a match.
Responding to webhooks
The default response to a webhook call contains just a simple text, "Accepted". The response is returned to the webhook's caller right away during the execution of the Custom Webhook module. You can easily test it like this:
Place the Custom Webhook module in your scenario.
Add a new webhook in the module's configuration.
Copy the webhook's URL to your clipboard.
Run the scenario - the Custom Webhook module should be waiting for the webhook call (see on the right)
Open a new browser window, paste the copied URL in the address bar and press Enter.
The Custom Webhook module will be triggered and the browser will display the following page:
These are default responses when the scenario does not contain the Webhook Response module:
HTTP status code | Body | |
Webhook accepted in the queue | 200 | Accepted |
Webhook queue full | 400 | Queue is full. |
If you wish to customize the webhook's response, employ the module Webhook Response. The configuration of the module contains two fields: Status and Body. The Status field should contain HTTP response status codes like 2xx for Success (e.g.200 for OK), 3xx for Redirection (e.g.307 for Temporary Redirect), 4xx for Client errors (e.g. 400 for Bad Request), etc. The Body field should contain anything that will be accepted by the webhook's call. It can be a simple text, HTML, XML, JSON, etc. It is advisable to set the Content-Type header to the corresponding mime type: text/plain for plain text, text/html for HTML, application/json for JSON, application/xml for XML, etc.
These are additional default responses when the scenario does contain the Webhook Response module:
HTTP status code | Body | |
Scenario encounters an error | 500 | Scenario failed to complete. |
The timeout for sending a response is 180 seconds. If the response is not available within that period, Make returns a '200 Accepted' status.
HTML Response example
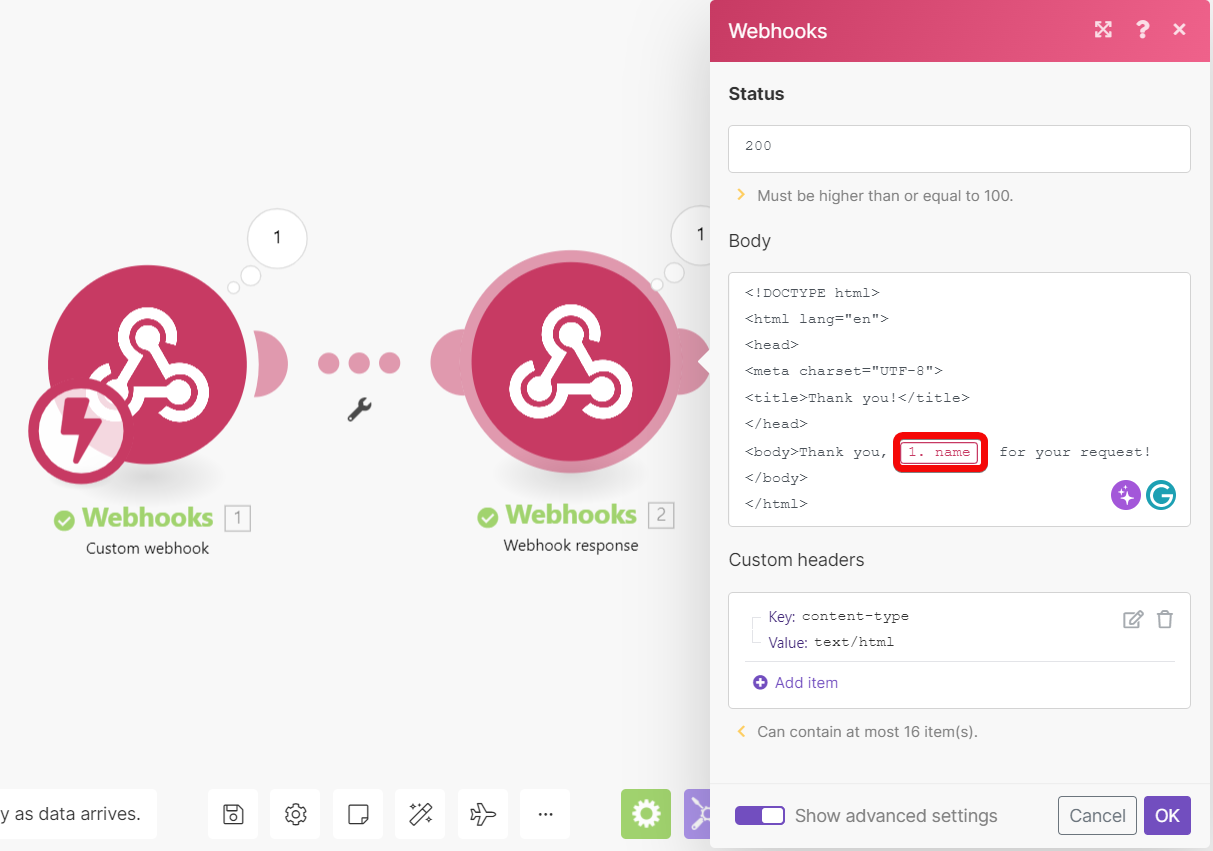
Configure the Webhook Response module as follows:
Status | 2xx success HTTP status code, e.g. | ||||
Body | HTML code, e.g.: <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thank you!</title>
</head>
<body>Thank you, {{1.name}}, for your request!
</body>
</html> | ||||
Custom headers |
|
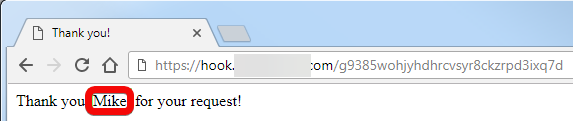
It will produce an HTML response that will be displayed like this in a web browser:
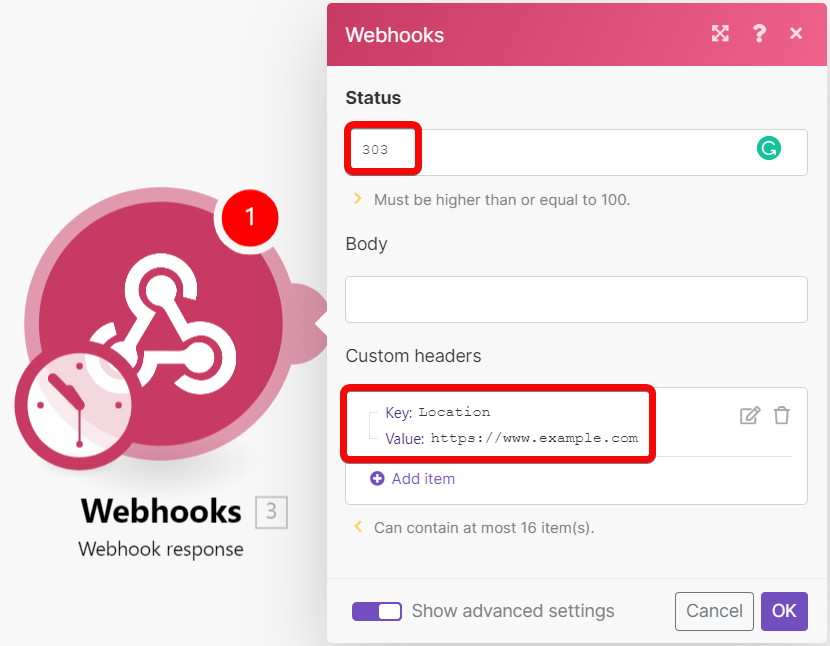
Redirect example
Configure the Webhook Response module as follows:
Status | 3xx redirection HTTP status code, e.g. | ||||
Custom headers |
|
Custom mailhook
Mailhook is an instant trigger module that can be triggered by sending an email to the email address generated by this module.
Mailhook attachment size limit
The maximum size of an email, including its attachments, that you send to a mailhook is 25 MB.
Example Of Use
Mailhook will monitor your incoming emails without the need to have a scheduled run of the scenario.
Add the Custom mailhook to your scenario (Webhooks > Custom mailhook).
Generate a mailhook email address, and copy the address to the clipboard.
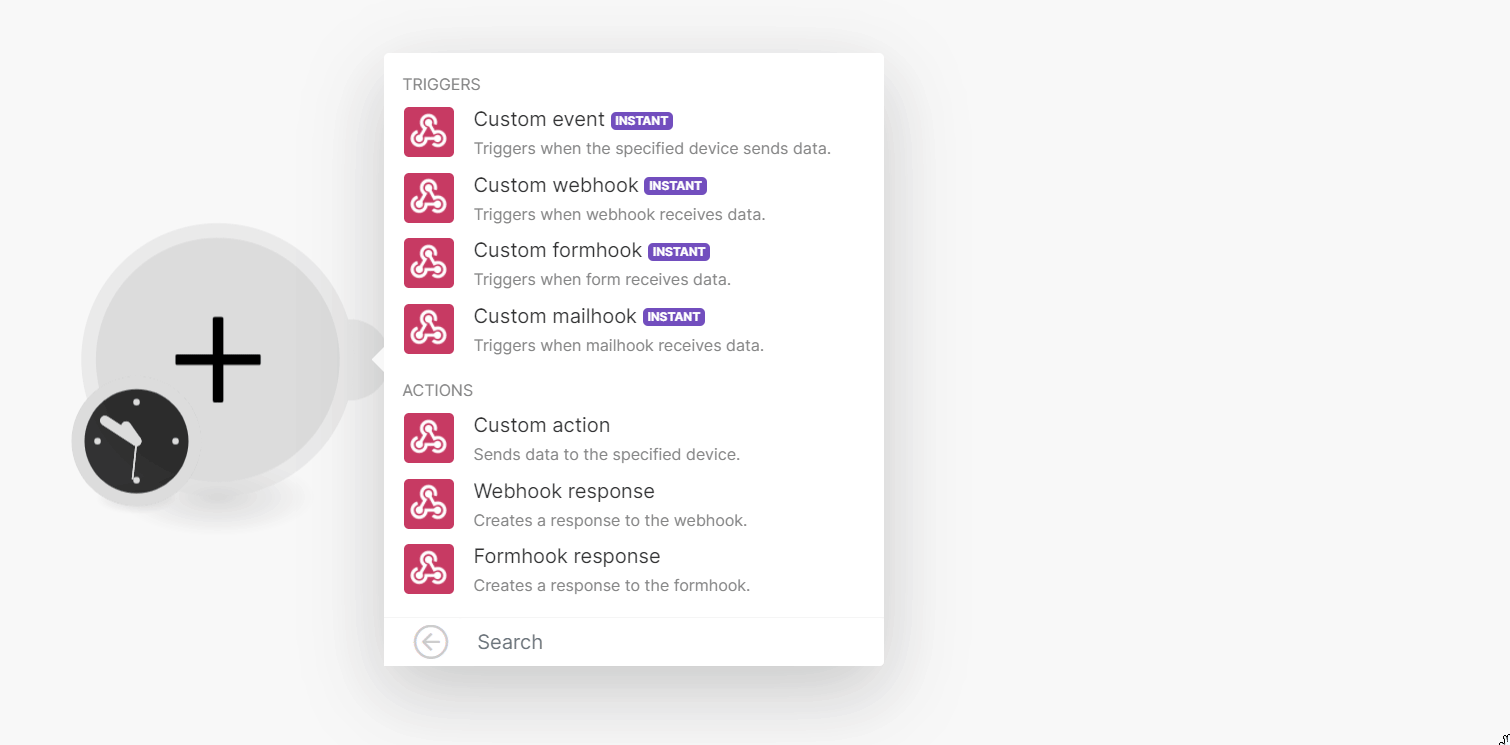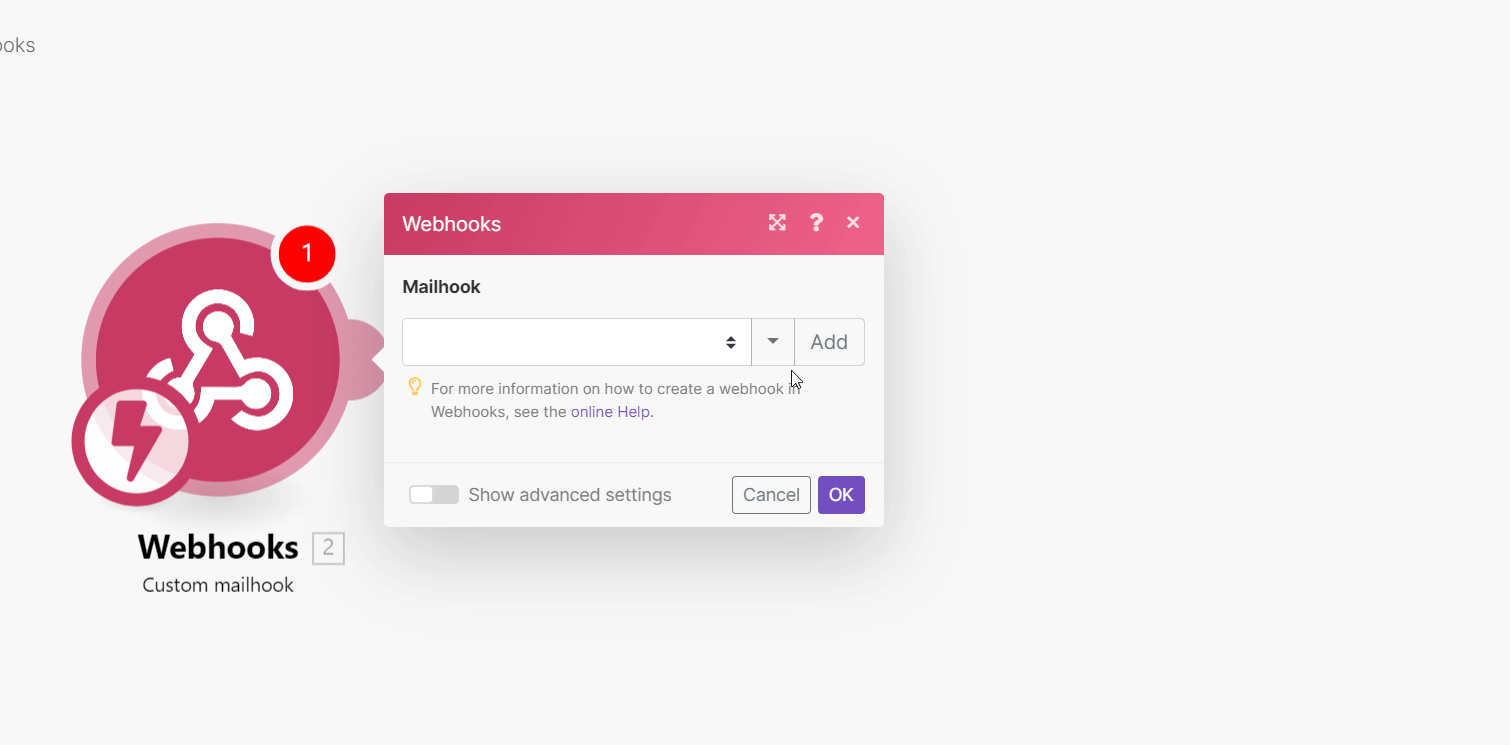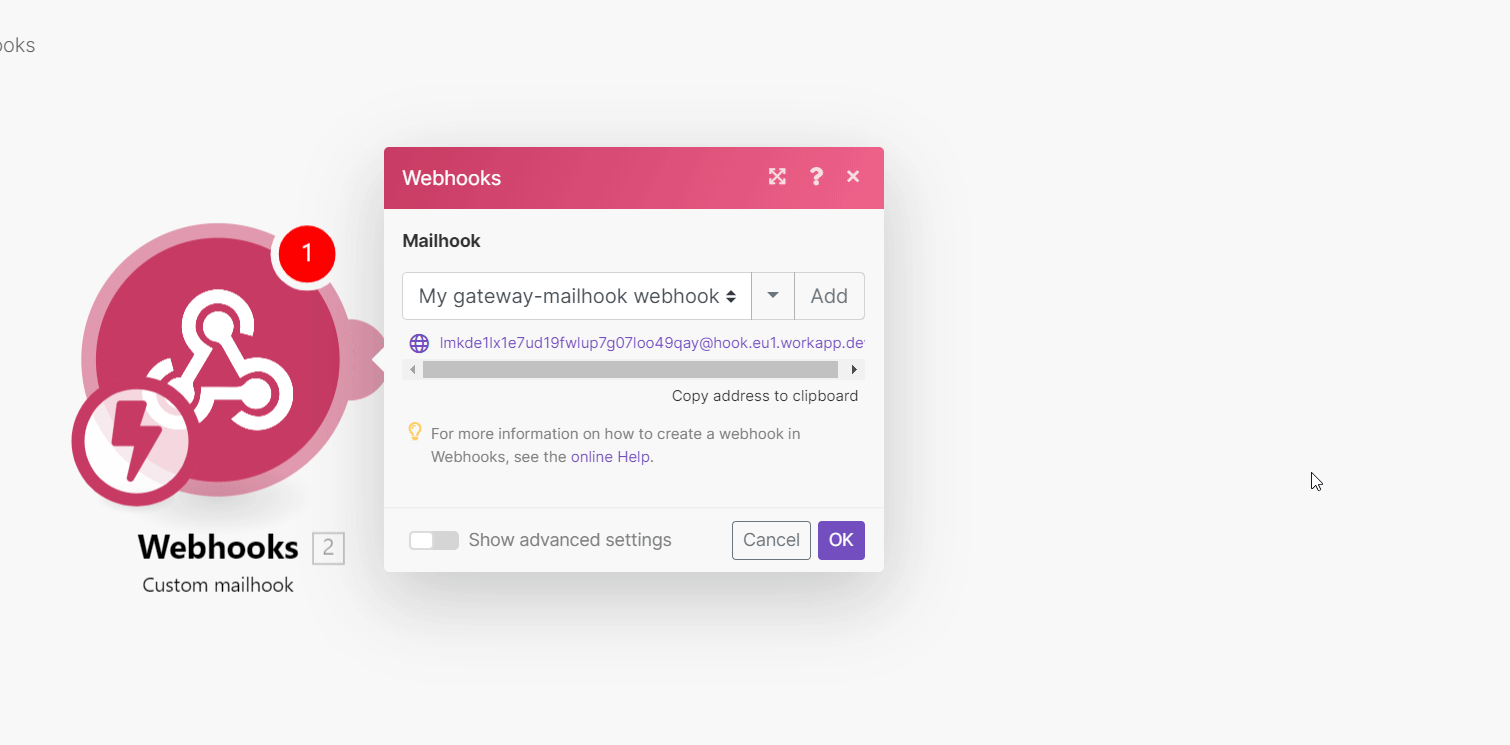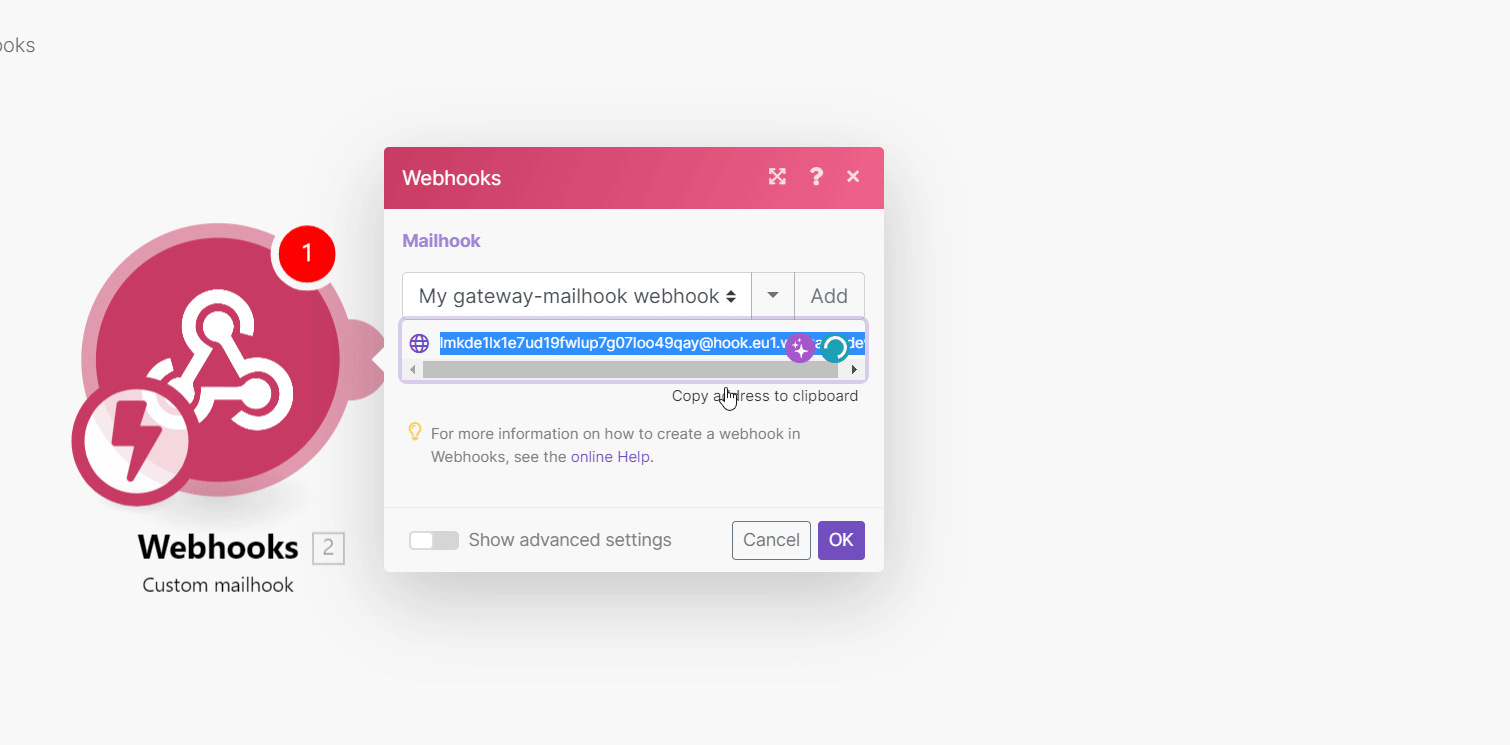
Save and run the scenario.
Open your email account settings, and configure forwarding. Use the email address generated by the Custom mailhook module in step 2 (above) as the forwarding address.
For Gmail:
Click the cogwheel (
 ) in the top-right corner, and then click See all settings.
) in the top-right corner, and then click See all settings.Open the Forwarding and POP/IMAP tab.
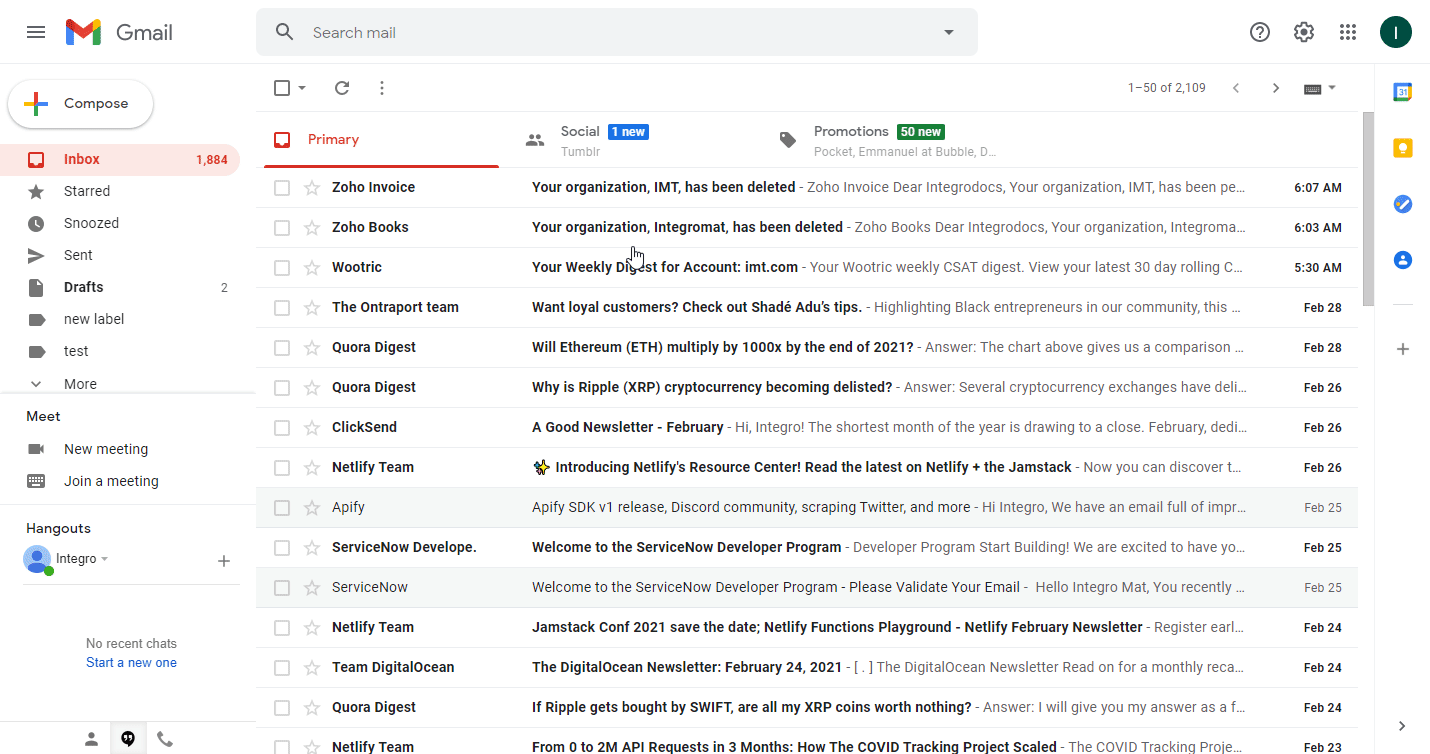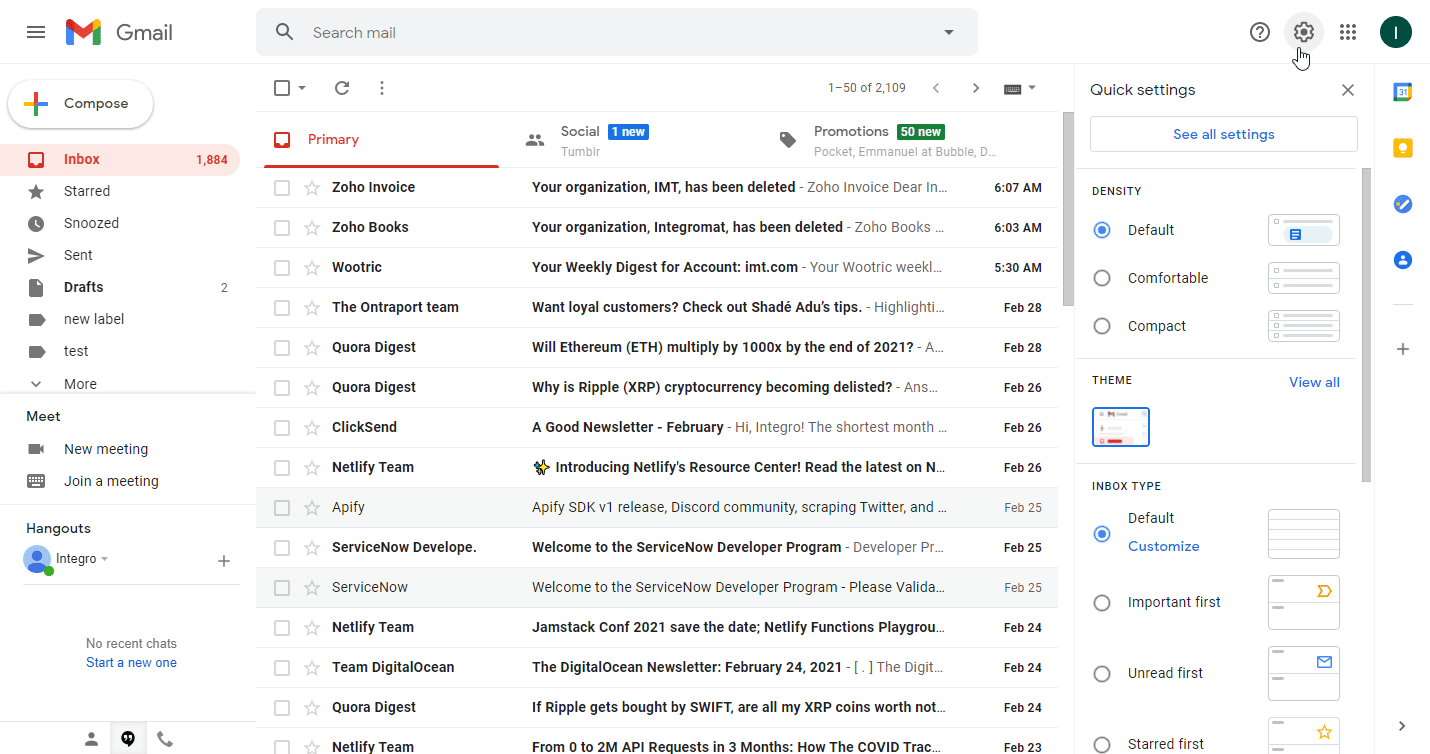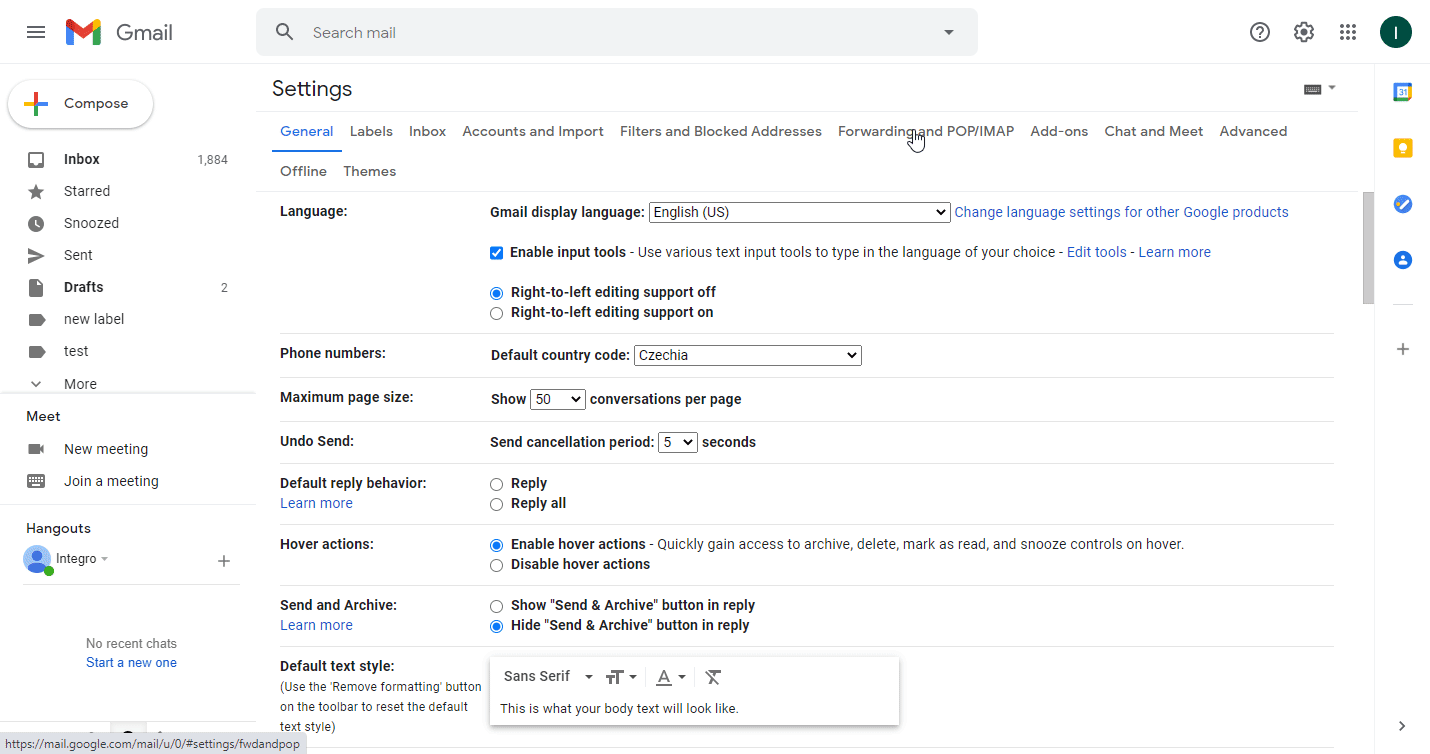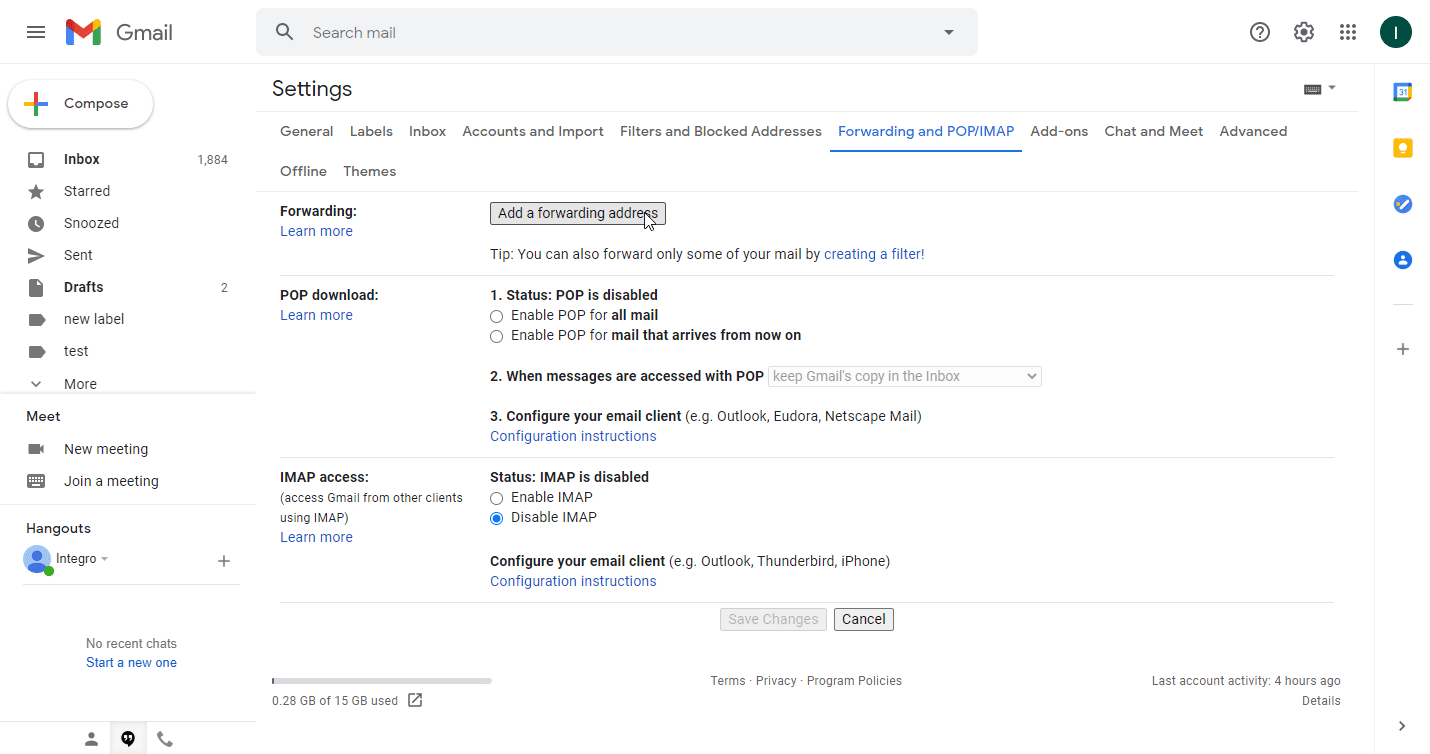

Click the Add a forwarding address button.
Enter the email address you have generated and copied in step 2 above, and click Next.
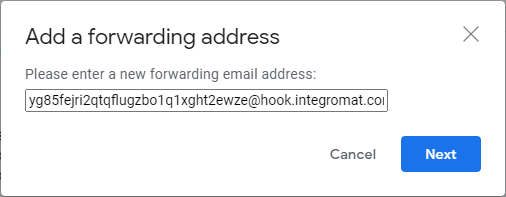
After that, a popup window will appear. Click Proceed.
A confirmation link has been sent to your mailhook. Run the custom mailhook module to see this code in the output under Bundle > Text.
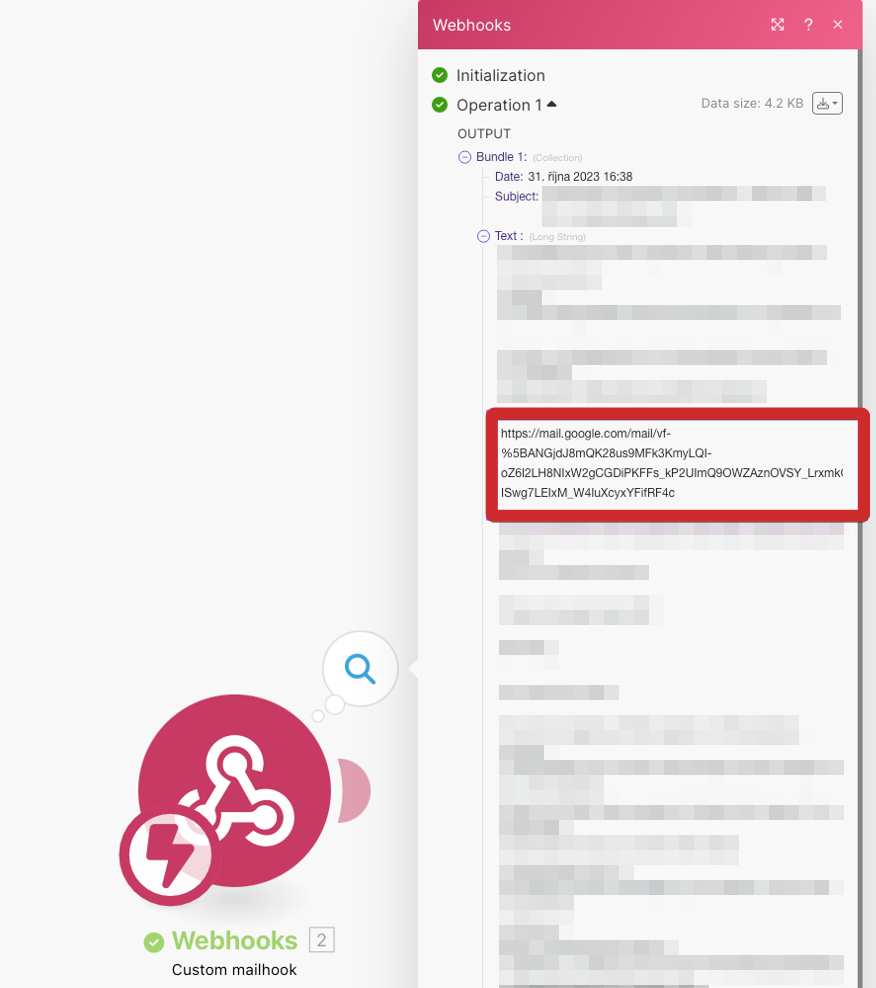
Note
If you use Gmail for work or school, you don't need to verify the forwarding address.
Enable the forwarding, and save changes.
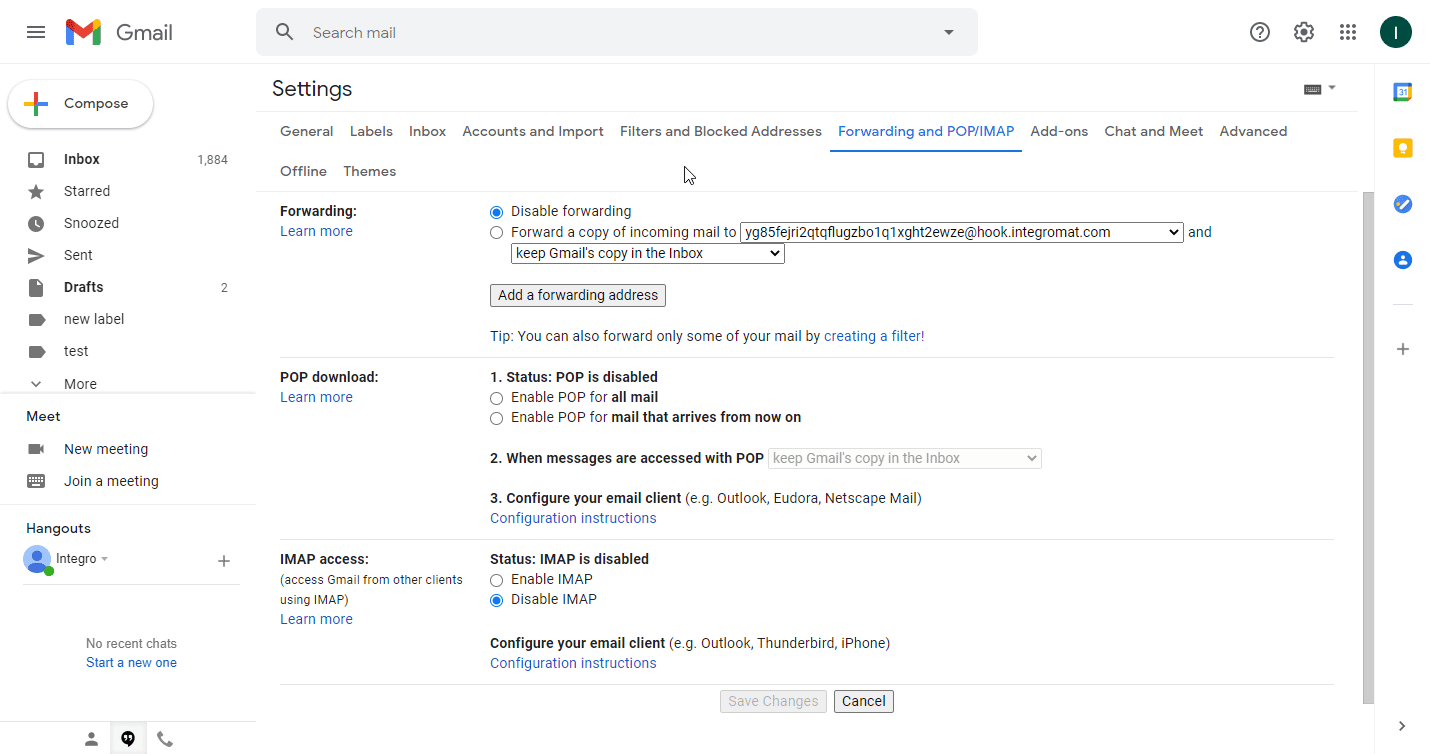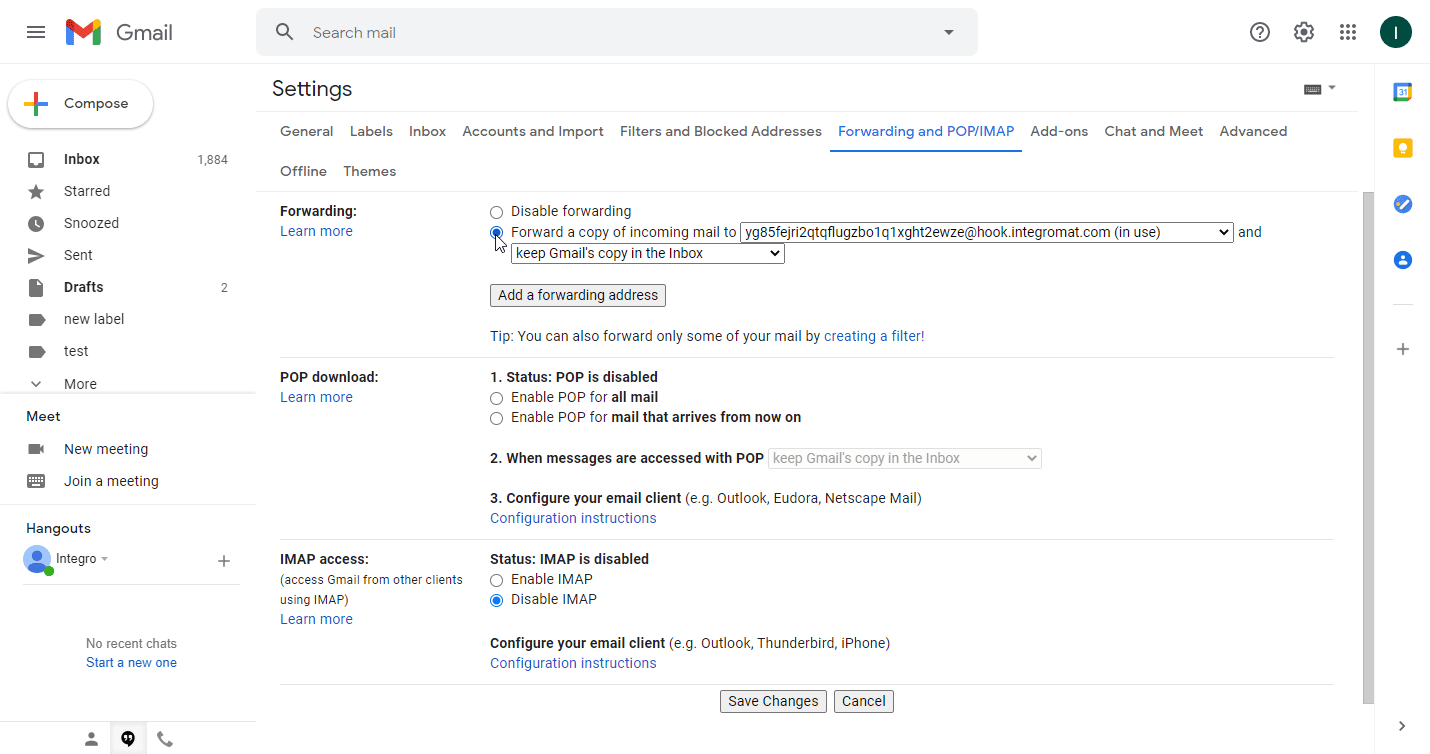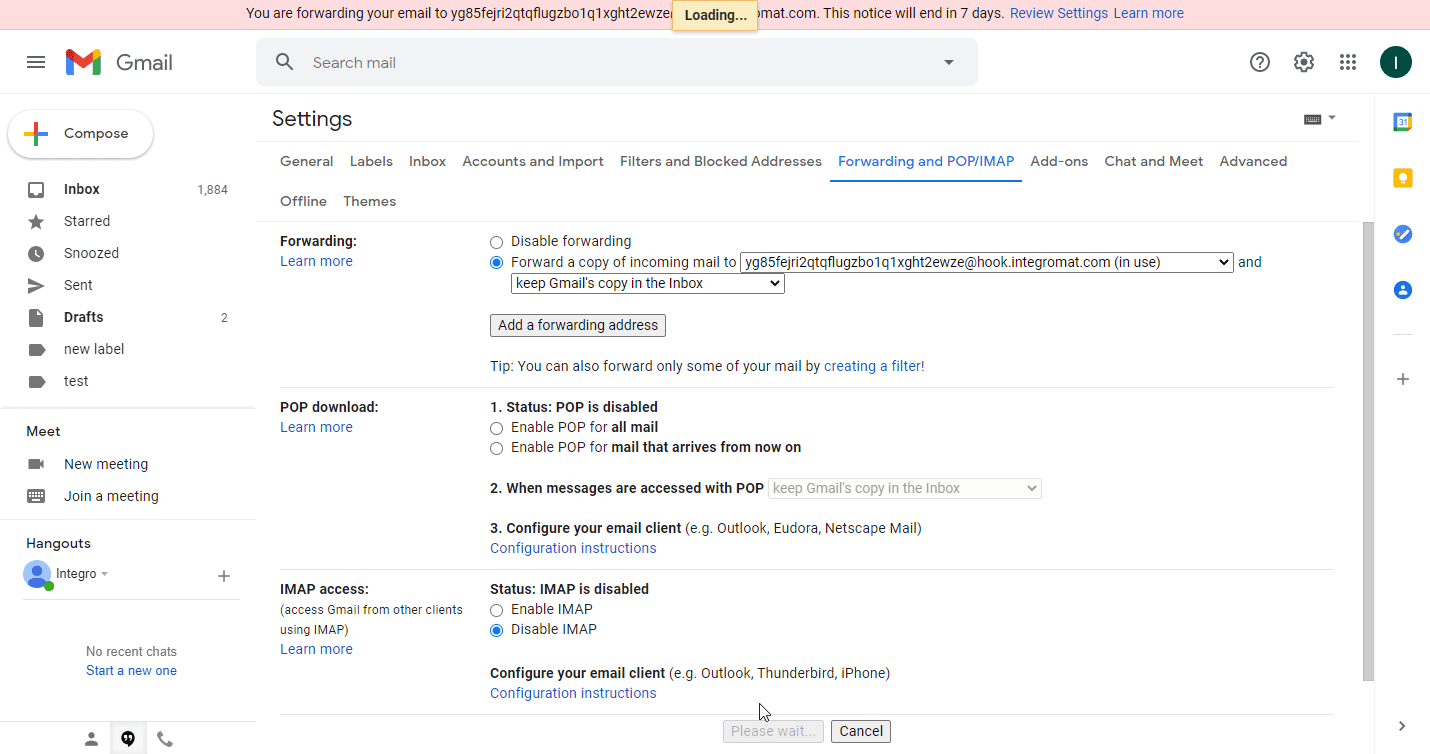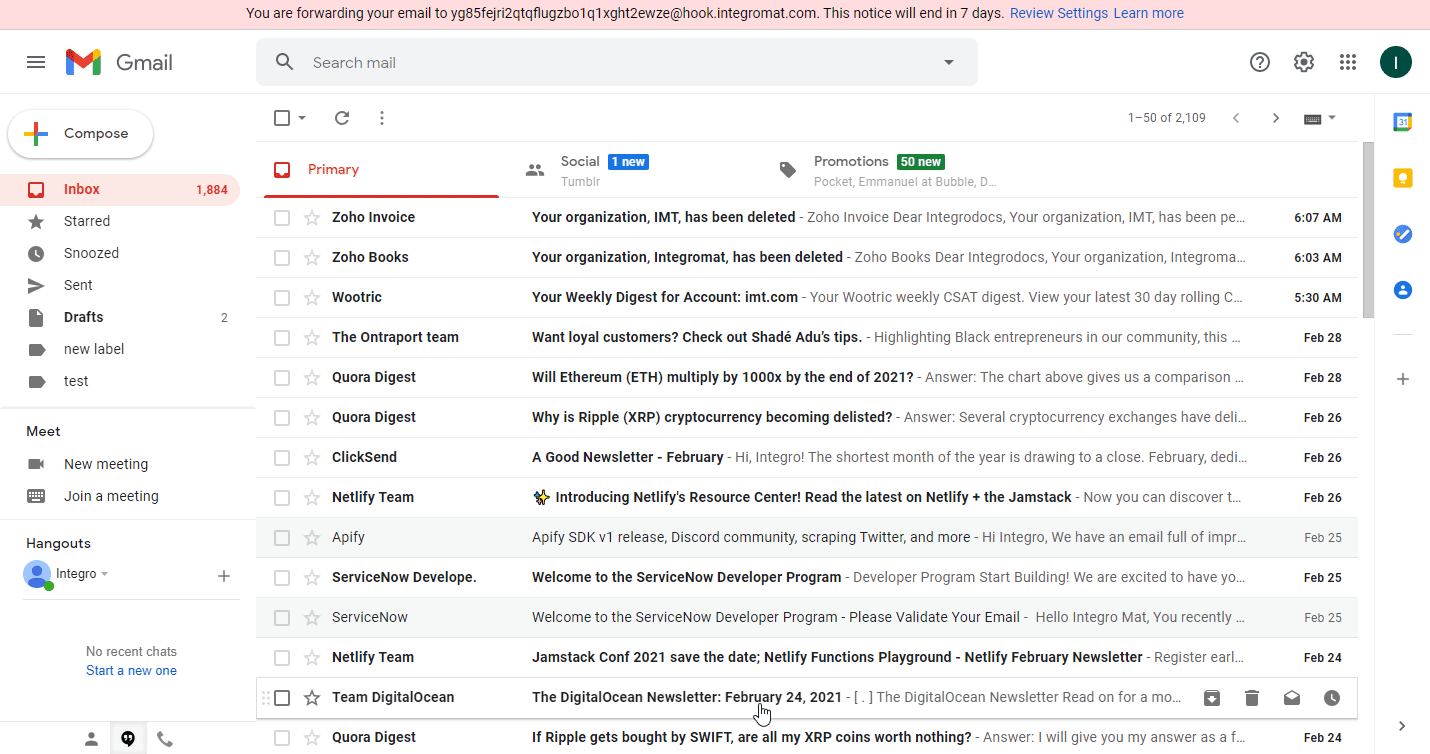
Add other desired modules to the scenario. Then save and activate the scenario
Now, every time a new email is received in your email account, the Custom mailhook module in your Make scenario is triggered and receives the email message data.
Tip
The sender and various recipient addresses (To: CC: and BCC:) are resolved in the data structure of the incoming mail. Reply-To: can be found in the Header section.
Webhook rate limit
Make can process up to 30 incoming webhook requests per second.
If you send more than 30 requests per second, the system returns an error with status code 429.
Troubleshooting Webhooks
Missing items in the mapping panel
If some items are missing in the mapping panel in the setup of the modules following the Webhooks > Custom Webhook module, click the Webhooks > Custom Webhook module to open its setup and click Re-determine data structure:
 |
Then follow the steps described in the section Determine the webhook's data structure.